路由模式
hash
url 中的 hash 部分不会引起页面的刷新
hashchange 监听 url 变化,浏览器导航栏的前进后退,a 标签,window.location 等方式触发事件
history
pushState 和 replaceState 改变 url 的 path 部分不会引起页面刷新
popchange 监听 url 变化,只有在浏览器导航栏的前进后退改变 url 时会触发事件,pushState/replaceState 不会触发 popstate 方法,需要进行拦截或重写 pushState/replaceState 来监听
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const _wr = function (type ) { const orig = history[type]; return function ( const e = new Event (type); e.arguments = arguments ; const rv = orig.apply (this , arguments ); window .dispatchEvent (e); return rv; }; }; history.pushState = _wr ("pushstate" );
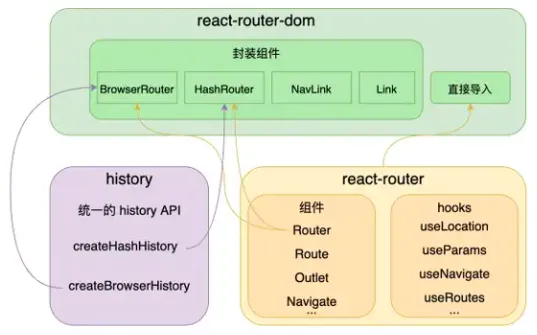
react-router 架构
BrowserHistory
监听路由变化的 listen 方法以及对应的清理监听 unlisten 方法
重写路由的 push 方法,自动触发 popstate 方法
window.location 获取参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 export const EventEmitter = ( const events = []; return { subscribe (fn ) { events.push (fn); return function ( events = events.filter ((handler ) => handler !== fn); }; }, emit (arg ) { events.forEach ((fn ) => fn && fn (arg)); }, }; }; const createBrowserHistory = ( const EventBus = EventEmitter (); let location = { pathname : "/" }; const handlePop = function ( const currentLocation = { pathname : window .location .pathname }; EventBus .emit (currentLocation); }; const push = (path ) => { const history = window .history ; history.pushState (null , "" , path); location = { pathname : path }; EventBus .emit (location); }; const listen = (listener ) => EventBus .subscribe (listener); window .addEventListener ("popstate" , handlePop); const history = { location, listen, push, }; return history; };
HashHistory
监听 hashchange
解析 hash 获取参数,比如 hash 部分是 #/a/b?c=1#/d,解析出 { hash: ‘#/d’, search: ‘?c=1’, pathname: ‘/a/b’ }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 const createHashHistory = ( const EventBus = EventEmitter (); let location = { pathname : "/" }; const handlePop = function ( const currentLocation = { pathname : window .location .hash .slice (1 ) }; EventBus .emit (currentLocation); }; const push = (path ) => (window .location .hash = path); const listen = (listener: Function ) => EventBus .subscribe (listener); window .addEventListener ("hashchange" , handlePop); const history = { location, listen, push, }; return history; };
react-router@6
v6 版本中移出了先前的 <Switch>,引入了新的替代者: <Routes>
<Routes> 和 <Route> 配合使用,用 <Routes> 包裹 <Route><Routes> 本质上调用 useRoutes 返回的对象, <Route> 相当于一个 case 语句,当 url 发生变化时,<Routes> 都会查看其所有子 <Route> 元素以找到最佳匹配并呈现组件withRouter: HOC ,非路由组件通过 withRouter 包裹来获取 history、location、match 信息
示例 App.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 export default function App ( return ( <div > {/* 设置路由链接 */} {/* className 接收一个函数,可以改变激活的类名 */} <Link className ="menu-item" to ="/about" > About </Link > <Link className ="menu-item" to ="/home" > Home </Link > {/* 注册路由 */} {/* 用 Routes 组件进行包裹*/} {/* Route 组件的 element 属性值为对应的组件*/} {/* caseSensitive 严格区分大小写*/} {/* 调用 useRoutes(),嵌入路由映射表 */} <Routes > <Route path ="/about" caseSensitive element ={ <About /> }></Route > <Route path ="/home" element ={ <Home /> }></Route > {/* Navigate 组件,页面渲染就显示对应组件,实现重定向效果 */} <Route path ="/" element ={ <Navigate to ="/about " /> }></Route > {useRoutes(routes)} </Routes > </div > ); }
index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 const root = createRoot (document .getElementById ("root" ));root.render ( <BrowserRouter > <App /> </BrowserRouter > );
Home.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 export default function Home ( return ( <div > <h3 > Home</h3 > <li > {/* 传递 params 参数,在路径后面用 / 进行拼接,useParams */} <Link to ={ `detail /${id }/${title }/${content }`}> {m.title}</Link > {/* 传递 search 参数,在路径后面用 ? 进行拼接,useSearchParams */} <Link to ={ `detail ?id =${id}&title =${title}&content =${content} `}> {title} </Link > {/* 传递 state 参数,添加 state 属性,值为一个对象,useLocation */} <Link to ="detail" state ={{ id , title , content }}> {title} </Link > </li > <div > {/* Outlet 路由占位符,表示"路由映射表"中匹配的组件将在此处展示 */} <Outlet /> </div > </div > ); }
Routes 标签 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 export interface RoutesProps { children ?: React .ReactNode ; location ?: Partial <Location > | string ; } export function Routes ({ children, location, }: RoutesProps ): React .ReactElement | null { return useRoutes (createRoutesFromChildren (children), location); } export function createRoutesFromChildren ( children : React .ReactNode RouteObject [] { let routes : RouteObject [] = []; React .Children .forEach (children, (element ) => { if (!React .isValidElement (element)) { return ; } if (element.type === React .Fragment ) { routes.push .apply ( routes, createRoutesFromChildren (element.props .children ) ); return ; } let route : RouteObject = { caseSensitive : element.props .caseSensitive , element : element.props .element , index : element.props .index , path : element.props .path , }; if (element.props .children ) { route.children = createRoutesFromChildren (element.props .children ); } routes.push (route); }); return routes; }
useRoutes
三个步骤: 路由上下文解析(父子路由)、路由匹配、路由渲染
解析上下文: 调用 useRoutes 的地方,如果是子路由调用,合并父路由的匹配信息,生成对应的 pathname
路由匹配: 调用 matchRoutes 返回 matches 数组,找到匹配的路由分支
路由渲染: 调用 _renderMatches 方法,通过 reduceRight 来形成 react 结构 elmenet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 function useRoutes ( routes : RouteObject [], locationArg ?: Partial <Location > | string React .ReactElement | null { invariant ( useInRouterContext (), `useRoutes() may be used only in the context of a <Router> component.` ); let { matches : parentMatches } = React .useContext (RouteContext ); let routeMatch = parentMatches[parentMatches.length - 1 ]; let parentParams = routeMatch ? routeMatch.params : {}; let parentPathname = routeMatch ? routeMatch.pathname : "/" ; let parentPathnameBase = routeMatch ? routeMatch.pathnameBase : "/" ; let parentRoute = routeMatch && routeMatch.route ; let locationFromContext = useLocation (); let location; if (locationArg) { let parsedLocationArg = typeof locationArg === "string" ? parsePath (locationArg) : locationArg; invariant ( parentPathnameBase === "/" || parsedLocationArg.pathname ?.startsWith (parentPathnameBase), `When overriding the location using \`<Routes location>\` or \`useRoutes(routes, location)\`, ` + `the location pathname must begin with the portion of the URL pathname that was ` + `matched by all parent routes. The current pathname base is "${parentPathnameBase} " ` + `but pathname "${parsedLocationArg.pathname} " was given in the \`location\` prop.` ); location = parsedLocationArg; } else { location = locationFromContext; } let pathname = location.pathname || "/" ; let remainingPathname = parentPathnameBase === "/" ? pathname : pathname.slice (parentPathnameBase.length ) || "/" ; let matches = matchRoutes (routes, { pathname : remainingPathname }); return __renderMatches ( matches && matches.map ((match ) => Object .assign ({}, match, { params : Object .assign ({}, parentParams, match.params ), pathname : joinPaths ([parentPathnameBase, match.pathname ]), pathnameBase : match.pathnameBase === "/" ? parentPathnameBase : joinPaths ([parentPathnameBase, match.pathnameBase ]), }) ), parentMatches ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 function matchRoutes ( routes : RouteObject [], locationArg : Partial <Location > | string , basename = "/" RouteMatch [] | null { let location = typeof locationArg === "string" ? parsePath (locationArg) : locationArg; let pathname = stripBasename (location.pathname || "/" , basename); if (pathname == null ) { return null ; } let branches = flattenRoutes (routes); rankRouteBranches (branches); let matches = null ; for (let i = 0 ; matches == null && i < branches.length ; ++i) { matches = matchRouteBranch (branches[i], pathname); } return matches; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 function _renderMatches ( matches : RouteMatch [] | null , parentMatches : RouteMatch [] = [] React .ReactElement | null { if (matches == null ) return null ; return matches.reduceRight ((outlet, match, index ) => { return ( <RouteContext.Provider children ={ match.route.element !== undefined ? match.route.element : <Outlet /> } value={{ outlet, matches: parentMatches.concat(matches.slice(0, index + 1)), }} /> ); }, null as React .ReactElement | null ); } export type Params <Key extends string = string > = { readonly [key in Key ]: string | undefined ; }; export interface RouteMatch <ParamKey extends string = string > { params : Params <ParamKey >; pathname : string ; pathnameBase : string ; route : RouteObject ; } interface RouteContextObject { outlet : React .ReactElement | null ; matches : RouteMatch []; } const RouteContext = React .createContext <RouteContextObject >({ outlet : null , matches : [], }); export { RouteContext as UNSAFE_RouteContext };
Outlet
内部渲染 RouteContext 的 outlet 属性,本质就是用了 useOutlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 const OutletContext = React .createContext < unknown > null ;export function useOutletContext<Context = unknown >(): Context { return React .useContext (OutletContext ) as Context ; } export function useOutlet (context ?: unknown React .ReactElement | null { let outlet = React .useContext (RouteContext ).outlet ; if (outlet) { return ( <OutletContext.Provider value ={context} > {outlet}</OutletContext.Provider > ); } return outlet; } export interface OutletProps { context ?: unknown ; } export function Outlet (props : OutletProps React .ReactElement | null { return useOutlet (props.context ); }
useNavigate
替代 history 的方案
navigate 默认是 history.push
naviaget(to, { replace: true }) 等同于 history.replace\
naviaget(number) 等同于 history.go
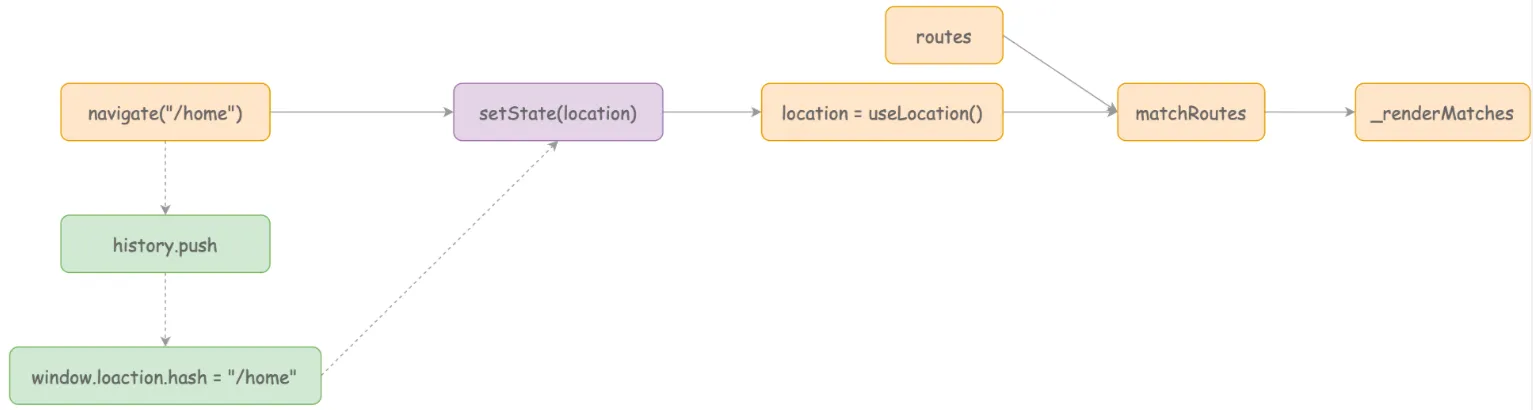
组件渲染过程总结
BrowserRouter 举例
路由更新,触发 listen 事件,新城新的 location 对象,更新 locationContext
useRoutes 消费 locationContext,locationContext 的变化会重新执行 useRoutes
重新执行内部调用 matchRoutes 和 _renderMatchers 找到新的渲染分支,渲染页面
v5 和 v6 对比
组件层面:
v5: Router Switch Route 结构,Router -> 传递状态,负责派发更新;Switch -> 匹配唯一路由;Route -> 真实渲染路由组件
v6: Router Routes Route 结构,Router 抽离了 context;Routes -> 形成路由渲染分支,渲染路由;Route 并非渲染真实路由,而是形成路由分支结构
使用层面:
v5: 嵌套路由,配置二级路由,需要写在具体的业务组件中
v6: 在外层统一配置路由结构,结构更清晰,通过 Outlet 来实现子路由的渲染,一定程度上类似于 vue 中的 view-router。搭配新的 api
原理层面:
v5: 本质在于 Route 组件,当路由上下文 context 改变的时候,Route 组件重新渲染,然后通过匹配来确定业务组件是否渲染
v6: 本质在于 Routes 组件,当 location 上下文改变的时候,Routes 重新渲染,重新形成渲染分支,然后通过 provider 方式逐层传递 Outlet,进行匹配渲染